The Martino group combines research in immunology, stem cells, and bioengineering, in order to understand the molecular and cellular mechanisms governing tissue repair and regeneration. Using the findings from the lab, the group aims at engineering novel regenerative strategies.
Research
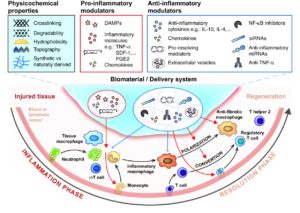
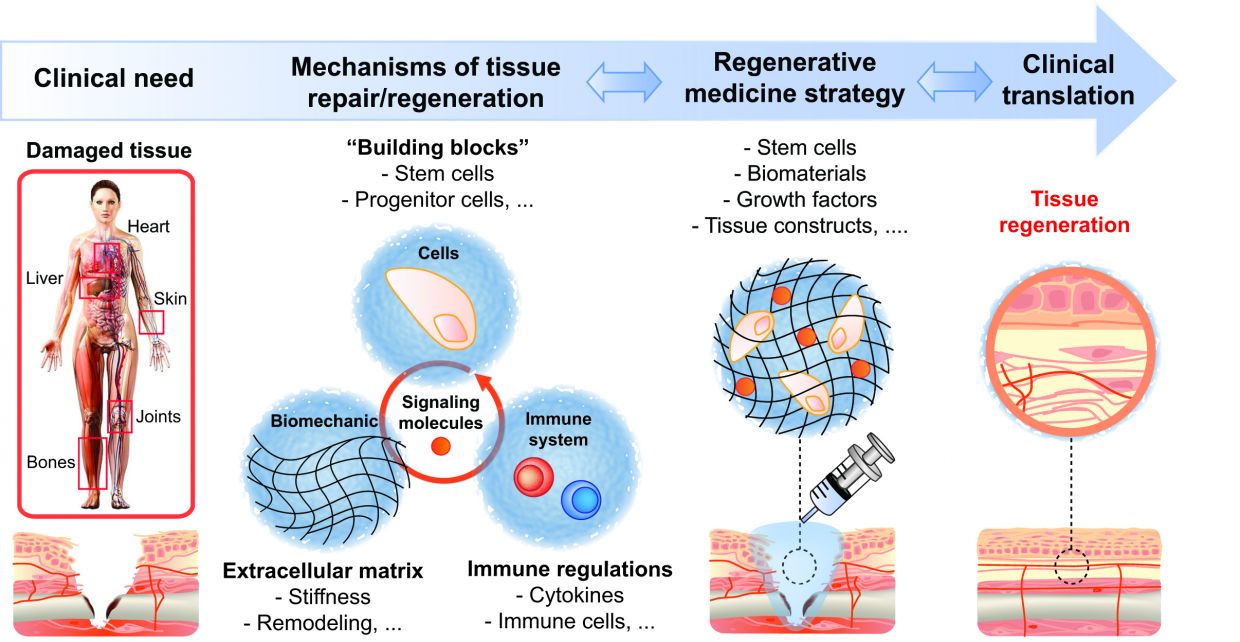
To design successful regenerative therapies and make regenerative medicine a more widespread reality, we need to understand how our body is able to create an environment suitable for regeneration. For instance, tissue injury and the healing process are usually accompanied with the activation of our immune system. The type of immune response, its duration, and the cells involved can considerably change the outcome of the healing process from incomplete restoration (causing scarring/ fibrosis and loss of function) to complete recovery (regeneration).
One of the main goals of the group is to reveal the key mechanisms by which the immune system leads to tissue repair or regeneration. Our research tools include genetically modified and chimeric mice as well as injury models in tissues such as bone, skin and muscle. Ultimately, the group seeks to engineer efficient regenerative strategies that integrate control of the immune system using various bioengineering approaches (such as biomaterials, protein engineering or immunoengineering).
Click here for Google Scholar link
Group Members



















Research Themes
1. Dissecting how the immune system modulates tissue repair and regeneration
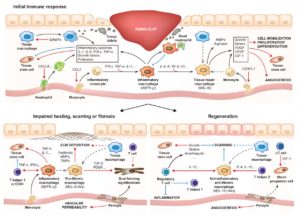
Tissue injury and the healing response is usually accompanied with the activation of the immune system. The type of immune response, its duration, and the cells involved can considerably change the outcome of the healing process from incomplete restoration (i.e. scarring/fibrosis and loss of function) to complete recovery (i.e. regeneration) [1] (Fig. 1).
Figure 1 (please click image for full size)
(please click image for full size)
Figure 2 (please click image for full size)
(please click image for full size)
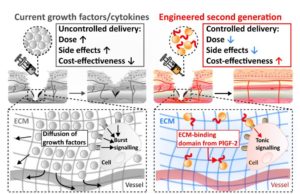
Stem cells and morphogens such as growth factors are obviously very promising for regenerative medicine. However, how can we actually create efficient and safe regenerative therapeutics based on stem cells or growth factors? While the first challenge is to find the right stem cell or the right morphogen for a particular application in regenerative medicine, the second challenge is to develop an appropriate and safe way to deliver these therapeutics. For example, stem cells need to survive and integrate in the host tissue after implantation, while morphogens need to signal in a controlled manner to stimulate endogenous regenerative pathways [3-9]. In addition, both stem cells and morphogens must display very limited side effects. To tackle these challenges, our group is developing delivery systems for stem cells and growth factors that are designed to maximize their therapeutic potential while limiting their side effects. For example, bone regeneration induced by mesenchymal stem cells has been significantly improved by limiting the inflammatory effect on stem cells [2]. Growth factor efficiency in promoting bone regeneration or chronic wound repair has been considerably enhanced by engineering growth factors to process a “built-in” delivery system which target the endogenous extracellular matrix in our tissue [7] (Fig. 4).
- Chronic wounds (diabetic and venous ulcers)
- Scar prevention
- Large musculoskeletal defects
- Ischemia-reperfusion
- Osteoarthrosis
References:
- Julier Z, Park AJ, Briquez PS, Martino MM, Promoting tissue regeneration by modulating the immune system. Acta Biomaterialia 53, 13-28 (2017).
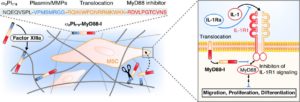
- Martino MM, Maruyama K, Kuhn GA, Satoh T, Takeuchi O, Muller R, Akira S, Inhibition of IL-1R1/MyD88 signalling promotes mesenchymal stem cell-driven tissue regeneration. Nature communications 7, 11051 (2016).
- Briquez PS, Clegg LE, Martino MM, Gabhann FM, Hubbell JA, Design principles for therapeutic angiogenic materials. Nature Reviews Materials 1, 15006 (2016).
- Martino MM, Briquez PS, Maruyama K, Hubbell JA, Extracellular matrix-inspired growth factor delivery systems for bone regeneration. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 94, 41-52 (2015).
- Martino MM, Brkic S, Bovo E, Burger M, Schaefer DJ, Wolff T, Gurke L, Briquez PS, Larsson HM, Gianni-Barrera R, Hubbell JA, Banfi A, Extracellular matrix and growth factor engineering for controlled angiogenesis in regenerative medicine. Frontiers in Bioengineering Biotechnology 3, 45 (2015).
- Briquez PS, Hubbell JA, Martino MM, Extracellular Matrix-Inspired Growth Factor Delivery Systems for Skin Wound Healing. Advances in Wound Care (New Rochelle) 4, 479-489 (2015).
- Martino MM, Briquez PS, Guc E, Tortelli F, Kilarski WW, Metzger S, Rice JJ, Kuhn GA, Muller R, Swartz MA, Hubbell JA, Growth factors engineered for super-affinity to the extracellular matrix enhance tissue healing. Science 343, 885-888 (2014).
- Martino MM, Briquez PS, Ranga A, Lutolf MP, Hubbell JA, Heparin-binding domain of fibrin(ogen) binds growth factors and promotes tissue repair when incorporated within a synthetic matrix. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 110, 4563-4568 (2013).
- Martino MM, Tortelli F, Mochizuki M, Traub S, Ben-David D, Kuhn GA, Muller R, Livne E, Eming SA, Hubbell JA, Engineering the growth factor microenvironment with fibronectin domains to promote wound and bone tissue healing. Science translational medicine 3, 100ra189 (2011).
Publications
Google scholar: https://scholar.google.com/citations?user=B4jJoH4AAAAJ&hl=en
Featured Publications
| Authors | Title | Published In |
|---|---|---|
Tan JL, Lash B, Karami R, Nayer B, Lu YZ, Piotto C, Julier Z, Martino MM. |
Restoration of the healing microenvironment in diabetic wounds with matrix-binding IL-1 receptor antagonist. |
Communications Biolology. 2021 Mar 26;4(1):422. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-01913-9. |
Ratnayake D, Nguyen PD, Rossello FJ, Wimmer VC, Tan JL, Galvis LA, Julier Z, Wood AJ, Boudier T, Isiaku AI, Berger S, Oorschot V, Sonntag C, Rogers KL, Marcelle C, Lieschke GJ, Martino MM, Bakkers J, Currie PD. |
Macrophages provide a transient muscle stem cell niche via NAMPT secretion. |
Nature. 2021 Mar;591(7849):281-287. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03199-7. |
Julier Z, Karami R, Nayer B, Lu YZ, Park AJ, Maruyama K, Kuhn GA, Müller R, Akira S, Martino MM. |
Enhancing the regenerative effectiveness of growth factors by local inhibition of interleukin-1 receptor signaling. |
Science Advances. 2020 Jun 12;6(24):eaba7602. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aba7602. eCollection 2020 Jun. |
Mochizuki M, Güç E, Park AJ, Julier Z, Briquez PS, Kuhn GA, Müller R, Swartz MA, Hubbell JA, Martino MM. |
Growth factors with enhanced syndecan binding generate tonic signalling and promote tissue healing. |
Nature Biomedical Engineering. 2020 Apr;4(4):463-475. doi: 10.1038/s41551-019-0469-1. |
Banfi A, Holnthoner W, Martino MM, Ylä-Herttuala S. |
Editorial: Vascularization for Regenerative Medicine. |
Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnolology. 2018 Nov 21;6:175. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2018.00175. eCollection 2018. |
Julier Z, Park AJ, Briquez PS, Martino MM. |
Promoting tissue regeneration by modulating the immune system. |
Acta Biomater. 2017 Apr 15;53:13-28. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2017.01.056. Epub 2017 Jan 22. |
More Publications
| Authors | Title | Published In |
|---|---|---|
Maruyama K, Kidoya H, Takemura N, Sugisawa E, Takeuchi O, Kondo T, Eid MMA, Tanaka H, Martino MM, Takakura N, Takayama Y, Akira S, Vandenbon A, Kumagai Y. |
Zinc Finger Protein St18 Protects against Septic Death by Inhibiting VEGF-A from Macrophages. |
Cell Reports. 2020 Jul 14;32(2):107906. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107906. |
Ren X, Zhao M, Lash B, Martino MM, Julier Z. |
Growth Factor Engineering Strategies for Regenerative Medicine Applications. |
Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnolology. 2020 Jan 21;7:469. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2019.00469. eCollection 2019. |
Maruyama K, Takayama Y, Sugisawa E, Yamanoi Y, Yokawa T, Kondo T, Ishibashi KI, Sahoo BR, Takemura N, Mori Y, Kanemaru H, Kumagai Y, Martino MM, Yoshioka Y, Nishijo H, Tanaka H, Sasaki A, Ohno N, Iwakura Y, Moriyama Y, Nomura M, Akira S, Tominaga M. |
The ATP Transporter VNUT Mediates Induction of Dectin-1-Triggered Candida Nociception. |
iScience. 2018 Aug 31;6:306-318. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2018.08.007. |
Hubbell JA, Martino MM, Briquez PSM. |
Protein-binding peptide isolated from placenta growth factor. |
|
Piotto C, Julier Z, Martino MM. |
Immune regulation of tissue repair and regeneration via miRNAs-new therapeutic target. |
Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2018 Jul 13;6:98. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2018.00098. eCollection 2018. |
Larouche J, Sheoran S, Maruyama K, Martino MM. |
Immune regulation of skin wound healing: mechanisms and novel therapeutic targets. |
Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2018 Jul 1;7(7):209-231. doi: 10.1089/wound.2017.0761. |
Li J, Tan J, Martino MM, Lui KO. |
Regulatory T-Cells: Potential regulator of tissue repair and regeneration. |
Front Immunol. 2018 Mar 23;9:585. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00585. eCollection 2018. |
Pilehvar-Soltanahmadi Y, Nouri M, Martino MM, Fattahi A, Alizadeh E, Darabi M, Rahmati-Yamchi M, Zarghami N. |
Cytoprotection, proliferation and epidermal differentiation of adipose tissue-derived stem cells on emu oil based electrospun nanofibrous mat. |
Exp Cell Res. 2017 Aug 15;357(2):192-201. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2017.05.015. Epub 2017 May 17. |
Maruyama K, Takemura N, Martino MM, Kondo T, Akira S. |
Netrins as prophylactic targets in skeletal diseases: A double-edged sword? |
Pharmacol Res. 2017 Aug;122:46-52. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2017.05.011. Epub 2017 May 30. |
Maruyama K, Takayama Y, Kondo T, Ishibashi KI, Sahoo BR, Kanemaru H, Kumagai Y, Martino MM, Tanaka H, Ohno N, Iwakura Y, Takemura N, Tominaga M, Akira S. |
Nociceptors boost the resolution of fungal osteoinflammation via the TRP channel-CGRP-Jdp2 axis. |
Cell Rep. 2017 Jun 27;19(13):2730-2742. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.06.002. |
Maruyama K, Kawasaki T, Hamaguchi M, Hashimoto M, Furu M, Ito H, Fujii T, Takemura N, Karuppuchamy T, Kondo T, Kawasaki T, Fukasaka M, Misawa T, Saitoh T, Suzuki Y, Martino MM, Kumagai Y, Akira S. |
Bone-protective functions of netrin 1 protein. |
J Biol Chem. 2016 Nov 11;291(46):23854-23868. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.738518. Epub 2016 Sep 28. |
Martino MM, Maruyama K, Kuhn GA, Satoh T, Takeuchi O, Müller R, Akira S. |
Inhibition of IL-1R1/MyD88 signalling promotes mesenchymal stem cell-driven tissue regeneration. |
Nat Commun. 2016; 7: 11051. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11051. Epub 2016 Mar 22. PMCID: PMC4804175. |
Briquez PS, Clegg LE, Martino MM, Gabhann FM, Hubbell JA. |
Design principles for therapeutic angiogenic materials. |
Nat Rev Mats 2016;1:15006. doi: 10.1038/natrevmats.2015.6. |
Briquez PS, Hubbell JA, Martino MM. |
Extracellular matrix-inspired growth factor delivery systems for skin wound healing. |
Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2015 Aug 1;4(8):479-489. doi: 10.1089/wound.2014.0603. |
Martino MM, Briquez PS, Maruyama K, Hubbell JA. |
Extracellular matrix-inspired growth factor delivery systems for bone regeneration. |
Adv Drug Deliv Rev; 2015 Nov 1;94:41-52. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2015.04.007. |
Najjar M, Manzoli V, Martino MM, Molano RD, Pileggi A, Camillo R, Hubbell JA, Tomei AA. |
Fibrin gels engineered with pro-angiogenic growth factors promote engraftment of pancreatic islets in extrahepatic sites in mice. |
Biotechnol Bioeng; 2015 Sep;112(9):1916-26. doi: 10.1002/bit.25589. |
Martino MM, Brkic S, Bovo E, Burger M, Schaefer DJ, Briquez PS, Gianni-Barrera R, Hubbell JA, Banfi A. |
Extracellular matrix and growth factor engineering for controlled angiogenesis in regenerative medicine. |
Front Bioeng Biotechnol; 2015 Apr 1;3:45. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2015.00045. |
Maruyama K, Fukasaka M, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O, Kondo T, Saitoh T, Martino MM, Akira S. |
AZI2 regulates bone mass by fine-tuning osteoclast survival. |
J Biol Chem; 2015 Apr 10;290(15):9377-86. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.631374. |
Julier Z, Martino MM, de Titta A, Jeanbart J, Hubbell JA. |
The immunological activity of the extra domain A of fibronectin (EDA) in agonizing TLR4 and inducing CD8+ T cell responses is cryptic and exposed by elastase 2. |
Sci Rep; 2015 Feb 24;5:8569. doi: 10.1038/srep08569. |
Vila OF, Martino MM, Nebuloni L, Kuhn G, Pérez-Amodio S, Müller R, Hubbell JA, Rubio N, Blanco J. |
Bioluminescent and μCT tomography imaging of bone repair induced by fibrin-binding growth factors. |
Acta Biomater; 2014 Oct;10(10):4377-89. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2014.05.028. |
Sacchi V, Mittermayr M, Hartinger J, Martino MM, Wolbank S, Hofmann A, Largo R, Marshall J, Groppa E, Gianni-Barrera R, Ehrbar M, Hubbell JA, Redl H, Banfi A. |
Sustained and highly tunable delivery of recombinant VEGF164 from optimized fibrin matrices ensures normal, stable and functional angiogenesis. |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A; 2014 May 13;111(19):6952-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1404605111. |
Martino MM, Briquez PS, Güç E, Tortelli F, Kilarski WW, Metzger S, Rice JJ, Kuhn GA, Müller R, Swartz MA, Hubbell JA. |
Growth factors engineered for super-affinity to the extracellular matrix enhance tissue healing. |
Science; 2014 Feb 21;343(6173):885-8. doi: 10.1126/science.1247663. |
Mosiewicz KA, Kolb L, van der Vlies AJ, Martino MM, Lienemann P, Hubbell JA, Ehrbar M, Lutolf MP. |
In situ cell fate manipulation by light-activated enzymatic hydrogel patterning. |
Nat Mater; 2013 Nov;12(11):1072-8. doi: 10.1038/nmat3766. |
Maruyama K, Uematsu S, Kondo T, Takeuchi O, Martino MM, Kawasaki T, Akira S. |
Strawberry notch homologue 2 plays a key role in fine-tuning osteoclast fusion. |
J Exp Med; 2013 Sep 23;210(10):1947-60. doi: 10.1084/jem.20130512. |