Untangling the Heart’s Genome: Now in 3D
Research led by Australian Regenerative Medicine Institute and Monash Biomedicine Discovery Institute (BDI) researchers at Monash University has combined cutting-edge genomics and 3D “gaming” modelling to understand how all genes are expressed in different parts of the heart, unveiling complex patterns and novel markers. To help visualise this new research, the team, led by Monash group leaders Associate Professor Mirana Ramialison and Professor Jose Polo in collaboration with Dr Fernando Rossello, has developed a powerful tool called 3D-cardiomics.
This work has been recently published in the Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology.
“One of the outstanding challenges in genomics research is understanding the physical context,” noted Associate Professor Ramialison, who has recently moved her research group to the Murdoch Children Research Institute to continue her work in heart development and genomics. “We can detect when gene expression is up or down-regulated in any number of tissues on a global level, but what is more complicated is understanding the spatial relationships in three dimensions. This is key to uncovering developmental and physiological processes of the heart, during both homeostasis and disease.”
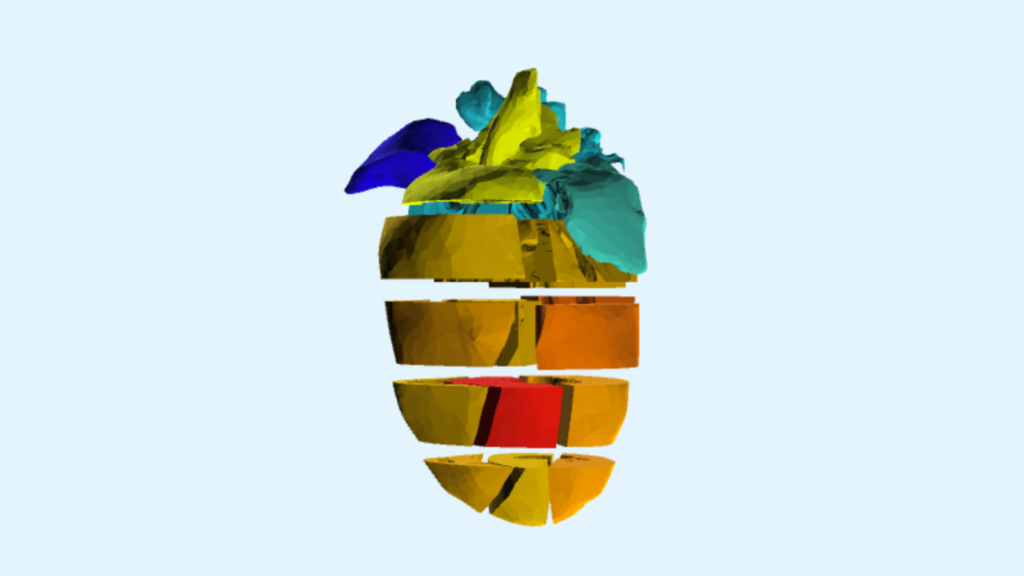
The research team microdissected and sequenced transcriptome-wide 18 anatomical sections of the adult mouse heart with this aim in mind. The study results unveiled known and novel genes that display complex spatial expression across the heart sub-compartments.
“Our spatial transcriptomic approach allowed us to demonstrate that most of the variability between the cardiac sections is due to the difference between the atria, major vessels and ventricles,” said Dr. Rossello. “These discoveries shed light on the complex genetic networks that regulate and coordinate cardiac function,” added Associate Professor Ramialison.
To take this work one step further, Honours student Nathalia Tan and undergraduate student Alex Tokolyi used “gaming” technology to generate 3D-cardiomics, a 3D model of the heart, offering cardiac and genomics researchers around the world an online interface to explore the data. This tool’s capabilities include visualising expression profiles of sufficiently expressed genes or groups of genes, corresponding correlated genes, and differential gene expression analysis.
“This is a fantastic and easy to use tool for anyone who wishes to explore how genes are regulated across the heart,” commented PhD student and lead author Monika Mohenska. The functionality of this easily accessible tool is beneficial for hypothesis building and the uncovering of new roles of gene expression in the mammalian heart.
“The project was a true collaboration between many branches of science and institutes across Australia and abroad, demonstrating how important it is to support collaborative and cross- disciplinary research,” said Professor Polo.
The paper was the culmination of an international collaboration involving researchers from:
- ARMI
- Monash Biomedicine Discovery Institute
- Monash Bioinformatics Platform
- The Faculty of Information Technology at Monash University
- CSIRO
- Murdoch Children’s Research Institute
- The University of Melbourne
- The Jackson Laboratory (USA)
- Academic Medical Centre (the Netherlands)
- Imperial College London (UK)
“This study provides a unique framework to explore gene expression in the mammalian heart and creates a springboard for the global biomedical research community to discover and identify spatially-restricted genes at an unprecedented resolution,” summarised Associated Professor Ramialison.
More information
About The Australian Regenerative Medicine Institute at Monash University
The Australian Regenerative Medicine Institute is one of the largest regenerative medicine and stem cell research organisations in the world and Australia’s only research institute specialising in regeneration and stem cells. Located on the Clayton campus of Monash University, researchers at ARMI focus on understanding the basic mechanisms of the regenerative process, aiming to eventually enable doctors to prevent, halt and reverse damage to vital organs due to disease, injury or genetic conditions.
About the Monash Biomedicine Discovery Institute at Monash University
Committed to making the discoveries that will relieve the future burden of disease, the newly established Monash Biomedicine Discovery Institute at Monash University brings together more than 120 internationally-renowned research teams. Our researchers are supported by world-class technology and infrastructure, and partner with industry, clinicians and researchers internationally to enhance lives through discovery.
About MCRI
The Murdoch Children’s Research Institute (MCRI) is the largest child health research institute in Australia committed to making discoveries and developing treatments to improve child and adolescent health in Australia and around the world. They are pioneering new treatments, trialling better vaccines and improving ways of diagnosing and helping sick babies, children and adolescents. It is one of the only research institutes in Australia to offer genetic testing to find answers for families of children with previously undiagnosed conditions.
